 资源预览
资源预览




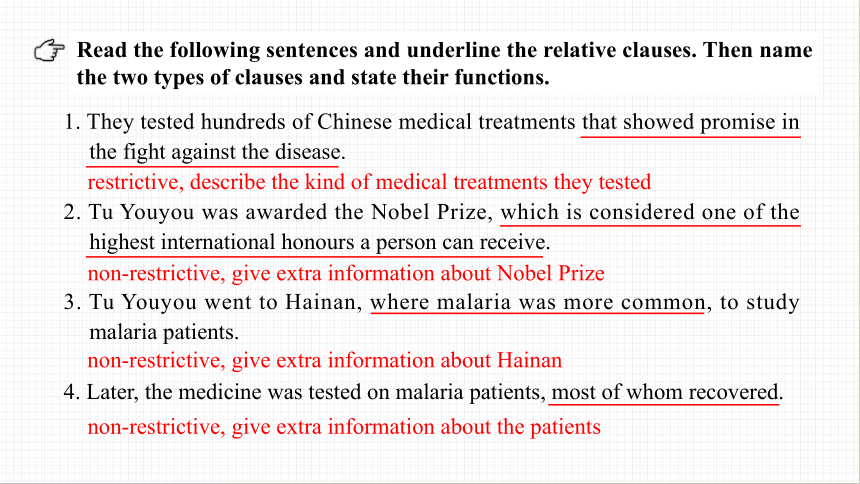

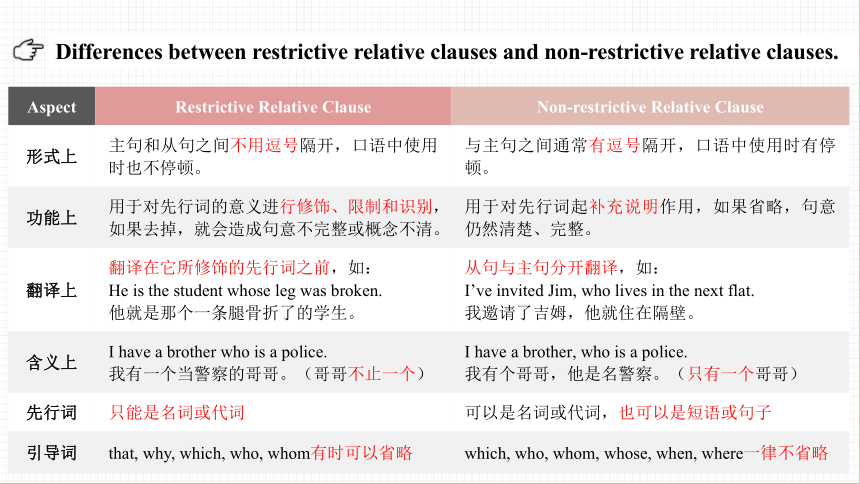

 资源预览
资源预览











